Environmental Innovations by IITs and Their Strategic Role in Building Aatmanirbhar Bharat
Indigenous technologies from IITs advance clean energy, waste management and green materials while helping Bharat move toward a stronger and more self reliant economy.
Total Views |

The world is undergoing a profound transformation with far-reaching consequences for economic, social and environmental systems. This new era, often described as the Intelligent Age, is being shaped by rapid advancements in AI, robotics, biotechnology, quantum computing and digital infrastructure. Just as the shift from an agricultural society to an industrial one altered the global order, the Intelligent Age is set to redefine how people live, work and connect with their surroundings.
Bharat stands at a critical juncture in its economic journey. Policy stability, deepening reforms, robust domestic consumption and a favourable demographic dividend have helped the country emerge as the fifth-largest global economy with a GDP of around four trillion dollars. Despite global disruptions, Bharat has maintained steady growth of seven to eight percent and continues to be the fastest-growing major economy. A strong emphasis on infrastructure and manufacturing has strengthened its global position. Coupled with a vast talent pool, an innate culture of innovation and decisive government support for digital transformation, Bharat is uniquely placed to lead in this new age.
Between 2018 and 2025, the IITs delivered sixteen landmark environmental technologies that promote national self-reliance, reduce dependence on foreign systems and reinforce India’s long-standing civilisational commitment to ecological balance. These innovations advance key national missions such as Aatmanirbhar Bharat, Swachh Bharat, the National Clean Air Programme, the National Water Mission, the Green Hydrogen and Biofuel Mission and Make in India along with rural development programmes.
1. Water Security and Indigenous Remediation Technologies
1.1 IIT Guwahati: Cyanobacteria-Based Lead Removal (2025)

A low-cost bioremediation process using Phormidium corium achieved 92.5 percent lead removal while lowering treatment costs by 40 to 60 percent.
Strategic relevance:
- Replaces expensive Western chemical technologies
- Enables affordable village-scale water treatment
- Strengthens national independence in water purification
1.2 IIT Guwahati: Fluoride and Iron Removal System (2025)

A community unit capable of treating twenty thousand litres per day at a cost of only twenty rupees per thousand litres.
Strategic relevance:
- Supports rural regions where fluorosis is widespread
- Demonstrates scalable and indigenous purification solutions
1.3 IIT Jodhpur: Clay Photocatalyst for Rural Water Purification (2018)

A sunlight-driven photocatalyst that is recoverable up to 99 percent and suitable for wastewater containing dyes and chemicals.
Strategic relevance:
- Offers low-cost purification for rural communities
- Reduces reliance on imported membranes and chemicals
2. Waste to Wealth and the Bio-Circular Economy
2.1 IIT Roorkee: Wheat-Straw Biodegradable Tableware (2025)

Transforms one hundred and twenty million tonnes of wheat straw into unbleached biodegradable tableware with a shelf life of eighteen to twenty four months.
Significance:
- Provides a direct solution to stubble burning
- Improves farmer income and strengthens the rural economy
- Counters imported single-use plastics
2.2 IIT Hyderabad: Sludge and Eggshell-Based Packaging Film (2025)

A biodegradable nanocomposite film with eighty percent improved water barrier capacity.
Strategic relevance:
- Converts urban sludge into a useful product
- Supports eco-friendly Make in India packaging alternatives
2.3 IIT Kharagpur: Cucumber-Peel Nanocellulose Packaging (2020)

A strong biodegradable film derived from vegetable waste.
Strategic relevance:
- Reflects India’s traditional ethos of waste utilisation
- Reduces the burden of plastic on the planet
2.4 IIT Hyderabad and KIIT: Agro-Waste Bio-Bricks (2019)

Bio-bricks made from sugarcane bagasse and straw that provide insulation and act as carbon sinks.
Strategic relevance:
- Reduces eighty four to one hundred and forty one million tonnes of agro-waste burned annually
- Enables low-cost rural housing in line with PM Awas Yojana
3. Clean Energy and a Low-Carbon Bharat
3.1 IIT BHU and Integral University: High-Oil Microalgae for Biofuels (2025)

A two-stage process that produces high-oil microalgae suitable for green biofuel production.
Strategic relevance:
- Reduces fossil fuel imports
- Supports the transition towards a low-carbon future
3.2 IIT Guwahati: Biological Conversion of Methane and CO₂ into Biofuels (2024)

Methanotrophic bacteria convert methane and carbon dioxide into methanol.
Strategic relevance:
- Converts greenhouse gases into useful energy
- Strengthens national energy independence
3.3 IIT Delhi: Flex-Fuel DME Technology for Diesel Vehicles (2022)

A collaboration with IOC and Ashok Leyland produced a DME diesel hybrid engine with negligible particulate matter emissions.
Strategic relevance:
- Reduces dependence on imported crude
- Lays the foundation for domestically produced clean transportation
4. Sustainable Construction and Indigenous Green Materials
4.1 IIT Kanpur: HaritArohi Kutir (2025)

A fire-resistant hut that can withstand temperatures up to eleven hundred degrees Celsius and support loads of thirteen hundred kilograms. It is built using crop residue.
Strategic relevance:
- Suitable for disaster-resilient homes in rural regions
- Offers eco-tourism potential linked to rural regeneration
- Combines traditional materials with modern engineering
4.2 IIT Indore: Cement-Free Geopolymer Concrete (2025)

Cuts emissions by eighty percent and reduces cost by twenty percent while requiring no water curing.
Significance:
- Positions India as a leader in green construction
- Reduces reliance on high-emission cement production
5. Water Clean-Up and Environmental Protection
5.1 IIT Roorkee: Microbial Consortium for Water Remediation (2025)

An eco-friendly biological treatment system licensed for industrial applications.
Strategic relevance:
- Supports the rejuvenation of drains, lakes and rivers
- Aligns with Namami Gange and national water restoration missions
5.2 IIT Kharagpur: Graphene-Based Oil-Water Separation (2025)

A system with ninety nine percent oil selectivity and over ninety percent recovery, requiring low energy input.
6. Agriculture and Food Security
6.1 IIT Roorkee: Clay-Based Ethylene Scavenger (2025)
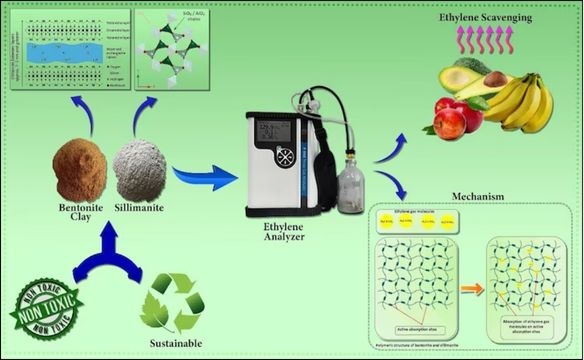
Extends the shelf life of fruits and vegetables by one week through eighty six percent ethylene absorption.
Strategic relevance:
- Reduces post-harvest losses
- Protects farmer income
- Provides an indigenous substitute for costly imported scavengers
In a Nutshell
The period from 2018 to 2025 shows that India’s environmental leadership is no longer dependent on imports. It is now created, engineered and manufactured within the nation. These sixteen IIT innovations enhance national resilience, environmental sovereignty, farmer prosperity, industrial competitiveness, rural empowerment and scientific independence. They reflect not only scientific progress but also a deeper ideological shift towards a self-reliant, culturally rooted and technologically confident Bharat.
Article by

Kewali Kabir Jain
Journalism Student, Makhanlal Chaturvedi National University of Journalism and Communication

